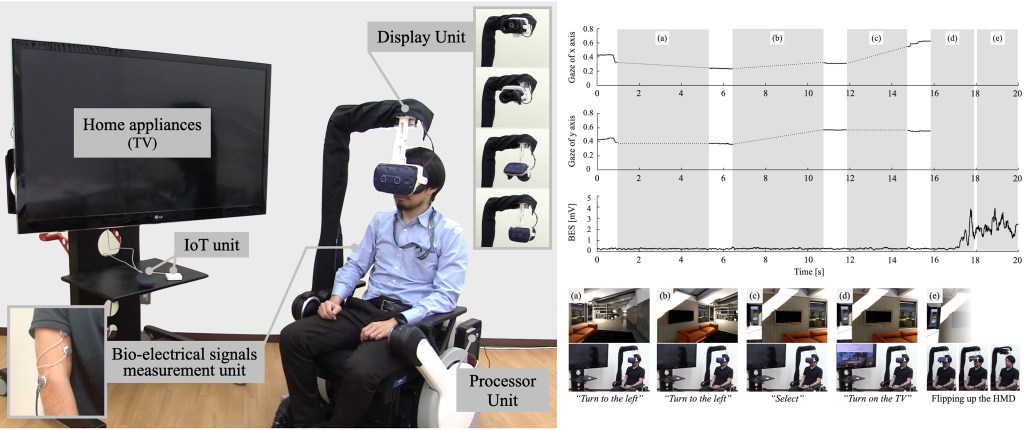
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) gradually make it difficult for the patients to move, breath, and express their will as their symptoms progress associated with motor neuron. It is important for the patients to be able to not only communicate their daily needs to someone such as family member of caregivers but also perform their daily activities and participate in society and fulfill social roles without constant support by other people. To improve their ability of independence, the purpose of this study is to develop a cybernic interface that can perform daily living tasks by transiting seamlessly between cyberspace and physical space based on the patient’s remaining voluntary motor functions, and confirm the basic performance of the developed interface.
The system consists of bio-electrical signals measurement unit, display unit, processor unit, and IoT unit. The system controlled the flipping up and down the head-mounted display (HMD) by estimating the intention of transition between cyberspace and physical space based on the bio-electrical signals of the forearm. When the HMD is attached to the user’s face, the user can move at the virtual environment, operate IoT device at the room of physical world via virtual environment, and select voice output for expressing own state by the gaze. To confirm the basic performance of the developed interface for performing daily living tasks by oneself, we conducted basic experiment with an able-bodied participant. As a result, the participant was able to flip up the HMD, move at virtual environment, and operate the TV and lock at the physical space without moving own body similar to ALS patients. In conclusion, we confirmed the basic performance of performing daily living tasks to improve the ability of independence for ALS patients. The cybernic interface that can connect central nervous system to cyberspace and physical space has a potential for removing constraints due to motor dysfunctions and spatial limitation.
Akira Uehara, Yoshiyuki Sankai, “Basic Study on Cybernic Interface for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients to Perform Daily living tasks by Transiting Seamlessly Between Cyberspace and Physical space,” Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integrations, pp. 314-319, 2024. [link]